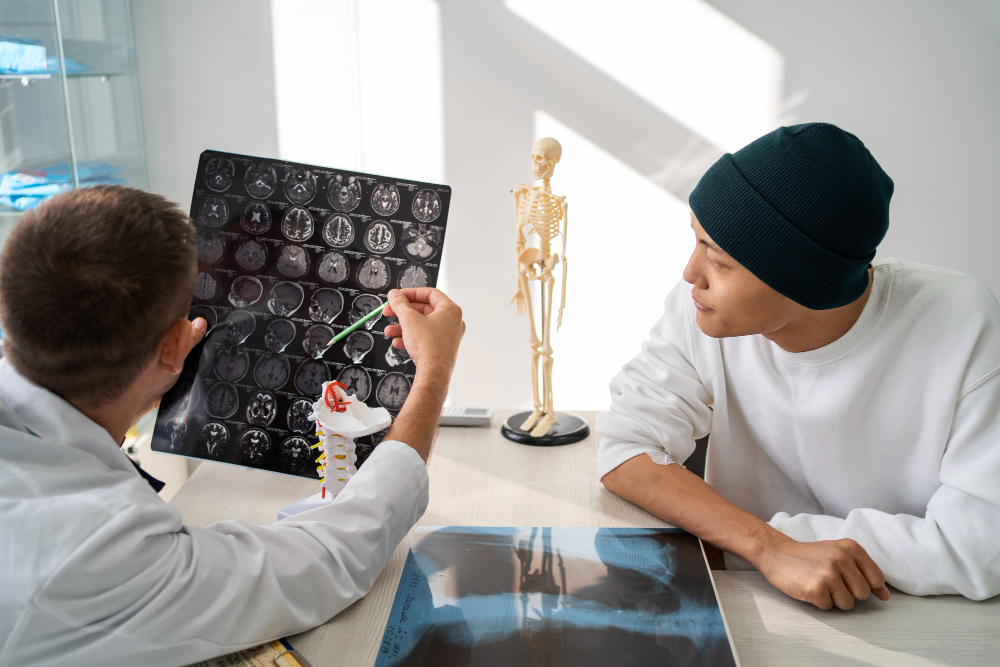
Brain stroke rehabilitation is a crucial process that helps stroke survivors regain independence and improve their quality of life. After a stroke, patients often experience physical, cognitive, and emotional challenges. A structured rehabilitation program, tailored to the individual’s needs, aims to maximize recovery and restore functional abilities.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a core component of stroke rehabilitation, focusing on improving mobility, balance, and muscle strength. Patients often have difficulty walking, moving limbs, or performing daily tasks due to stroke-induced weakness or paralysis. Therapists use exercises and techniques to enhance motor skills, coordination, and range of motion. Assistive devices such as walkers or braces may also be employed to aid mobility.
Speech and Language Therapy
A stroke can affect communication skills, leading to speech difficulties or problems with understanding language. Speech and language therapy helps patients regain the ability to speak, read, write, and comprehend language. This therapy also addresses issues related to swallowing, which can be impaired after a stroke.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy focuses on helping patients perform everyday tasks, such as dressing, eating, and bathing. Therapists work with patients to develop new strategies for performing these activities, often using adaptive equipment or modifying tasks to match the individual’s capabilities.
Neuropsychological Support
Stroke survivors may also face cognitive challenges, including memory loss, attention deficits, or emotional instability. Neuropsychologists provide cognitive therapy to improve thinking skills, while counseling can help address emotional and psychological issues, such as depression or anxiety.